Research Area C - Publications 2010
11-Jan-2011
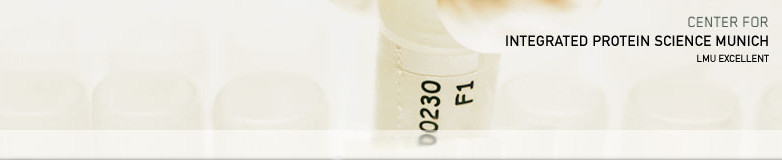
Higher-order multi-protein complexes such as RNA polymerase II (Pol II) complexes with transcription initiation factors are often not amenable to X-ray structure determination. Here, we show that protein cross-linking coupled to mass spectrometry (MS) has now sufficiently advanced as a tool to extend the Pol II structure to a 15-subunit, 670 kDa complex of Pol II ...
01-Dec-2010
The elongation cycle of protein synthesis involves the delivery of aminoacyl-transfer RNAs to the aminoacyl-tRNA-binding site (A site) of the ribosome, followed by peptide-bond formation and translocation of the tRNAs through the ribosome to reopen the A site1, 2. The translocation reaction is catalysed by elongation factor G (EF-G) in a GTP-dependent manner3. ...
29-Nov-2010
Proteins, 2010, Volume 79, Issue 2, pages 558–568, DOI: 10.1002/prot.22903 published on 29.11.2010
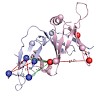
Structural Maintenance of Chromosomes (SMC) proteins are essential for a wide range of processes including chromosome structure and dynamics, gene regulation, and DNA repair. While bacteria and archaea have one SMC protein that forms a homodimer, eukaryotes possess three distinct SMC complexes, consisting of heterodimeric pairs of six different SMC proteins. SMC ...
23-Nov-2010

Today, the European Molecular Biology Organization (EMBO) announced the selection of 21 of Europeʼs most talented young researchers as 2010 beneficiaries of the EMBO Young Investigator Programme. We congratulate CIPSM's Daniel Wilson to be one of them. Daniel received the EMBO Young Investigators Award for his development and research of new antiobiotics that ...
19-Nov-2010

To initiate gene transcription, RNA polymerase II (Pol II) requires the transcription factor IIB (B). Here we present the crystal structure of the complete Pol II–B complex at 4.3 Å resolution, and complementary functional data. The results indicate the mechanism of transcription initiation, including the transition to RNA elongation. Promoter DNA is positioned ...
17-Nov-2010

Molecular motors have inspired many avenues of research for nanotechnology but most molecular motors studied so far allow only unidirectional movement. The archaeal RNA-exosome is a reversible motor that can either polymerize or degrade an RNA strand, depending on the chemical environments. We developed a single molecule fluorescence assay to analyze the real ...
16-Nov-2010
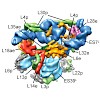
Protein synthesis in all living organisms occurs on ribonucleoprotein particles, called ribosomes. Despite the universality of this process, eukaryotic ribosomes are significantly larger in size than their bacterial counterparts due in part to the presence of 80 r proteins rather than 54 in bacteria. Using cryoelectron microscopy reconstructions of a translating ...
16-Nov-2010

Protein biosynthesis, the translation of the genetic code into polypeptides, occurs on ribonucleoprotein particles called ribosomes. Although X-ray structures of bacterial ribosomes are available, high-resolution structures of eukaryotic 80S ribosomes are lacking. Using cryoelectron microscopy and single-particle reconstruction, we have determined the structure ...
12-Nov-2010
PNAS, 2010, vol. 107 no. 48 20720-20725, doi: 10.1073/pnas.1008894107 published on 12.11.2010
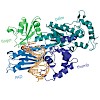
Heterocyclic aromatic amines produce bulky C8 guanine lesions in vivo, which interfere and disrupt DNA and RNA synthesis. These lesions are consequently strong replication blocks. In addition bulky adducts give rise to point and frameshift mutations. The translesion synthesis (TLS) DNA polymerase Eta is able to bypass slowly C8 bulky adduct lesions such as the ...
12-Nov-2010
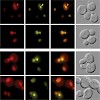
Multiple DNA associated processes such as DNA repair, replication and recombination are crucial for the maintenance of genome integrity. Here, we show a novel interaction between the transcription elongation factor Bur1-Bur2 and replication protein A (RPA), the eukaryotic single-stranded DNA binding protein with functions in DNA repair, recombination, and ...
10-Nov-2010

We have previously reported that star shaped poly(ethylene oxide-stat-propylene oxide) macromers with 80% EO content and isocyanate functional groups at the distal ends [NCO-sP(EO-stat-PO)] can be used to generate coatings that are non-adhesive but easily functionalized for specific cell adhesion. In the present study, we investigated whether the ...
24-Oct-2010
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, online article

Classic nuclear export signals (NESs) confer CRM1-dependent nuclear export. Here we present crystal structures of the RanGTP−CRM1 complex alone and bound to the prototypic PKI or HIV-1 Rev NESs. These NESs differ markedly in the spacing of their key hydrophobic (Φ) residues, yet CRM1 recognizes them with the same rigid set of five Φ pockets. The different Φ ...
20-Oct-2010
JACS, 2010, 132 (44), pp 15692–15698, DOI: 10.1021/ja1064608 published on 20.10.2010

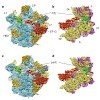
Ph1500 is a homohexameric, two-domain protein of unknown function from the hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrococcus horikoshii. The C-terminal hexamerization domain (Ph1500C) is of particular interest, as it lacks sequence homology to proteins of known structure. However, it resisted crystallization for X-ray analysis, and proteins of this size (49 kDa) present a ...
08-Oct-2010
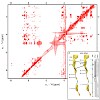
Specific regulatory nascent chains establish direct interactions with the ribosomal tunnel, leading to translational stalling. Despite a wealth of biochemical data, structural insight into the mechanism of translational stalling in eukaryotes is still lacking. Here we use cryo-electron microscopy to visualize eukaryotic ribosomes stalled during the translation of ...
06-Oct-2010
The Journal of Biological Chemistry, online article

Spt6 is an essential transcription elongation factor and histone chaperone that binds the C-terminal repeat domain (CTD) of RNA polymerase (Pol) II. We show here that Spt6 contains a tandem SH2 domain with a novel structure and CTD-binding mode. The tandem SH2 domain binds to a serine 2-phosphorylated CTD peptide in vitro, whereas its N-terminal SH2 subdomain, ...
01-Oct-2010
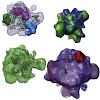
RNA polymerase III (Pol III) transcribes short RNAs required for cell growth. Under stress conditions, the conserved protein Maf1 rapidly represses Pol III transcription. We report the crystal structure of Maf1 and cryo-electron microscopic structures of Pol III, an active Pol III-DNA-RNA complex, and a repressive Pol III-Maf1 complex. Binding of DNA and RNA ...
13-Sep-2010
Langmuir, 2010, pp 15472–15480, DOI: 10.1021/la103065x published on 13.09.2010
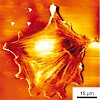
Despite tremendous progress in recent years, nanopatterning of hydrated polymeric systems such as hydrogels still represents a major challenge. Here, we employ block copolymer nanolithography to arrange gold nanoparticles on a solid template, followed by the transfer of the pattern to a polymeric hydrogel. In the next step, these nanoparticles serve as specific ...
05-Sep-2010
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, 2010, 17, doi:10.1038/nsmb.1903 published on 05.09.2010
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, online article

We present genome-wide occupancy profiles for RNA polymerase (Pol) II, its phosphorylated forms and transcription factors in proliferating yeast. Pol II exchanges initiation factors for elongation factors during a 5′ transition that is completed 150 nucleotides downstream of the transcription start site (TSS). The resulting elongation complex is composed of all ...
27-Aug-2010
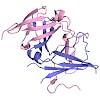
The eukaryotic RNA polymerases Pol I, II, and III use different promoters to transcribe different classes of genes. Promoter usage relies on initiation factors, including TFIIF and TFIIE, in the case of Pol II. Here, we show that the Pol I-specific subunits A49 and A34.5 form a subcomplex that binds DNA and is related to TFIIF and TFIIE. The N-terminal regions of ...
27-Aug-2010
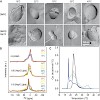
Hsp12 of S. cerevisiae is upregulated several 100-fold in response to stress. Our phenotypic analysis showed that this protein is important for survival of a variety of stress conditions, including high temperature. In the absence of Hsp12, we observed changes in cell morphology under stress conditions. Surprisingly, in the cell, Hsp12 exists both as a soluble ...
13-Aug-2010
Journal of Molecular Biology, online article
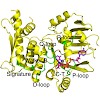
ATP-binding cassette (ABC) enzymes are involved in diverse biological processes ranging from transmembrane transport to chromosome cohesion and DNA repair. They typically use ATP hydrolysis to conduct energy-dependent biological reactions. However, the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator and the DNA repair protein Rad50 can also catalyze the ...
28-Jul-2010
Protein Science, 2010, DOI: 10.1002/pro.476, 11 published on 28.07.2010
Protein Science, online article
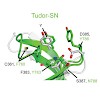
Post-translational modifications of histone tails are among the most prominent epigenetic marks and play a critical role in transcriptional control at the level of chromatin. The Polycomblike (Pcl) protein is part of a histone methyltransferase complex (Pcl-PRC2) responsible for high levels of histone H3 K27 trimethylation. Studies in Drosophila larvae suggest ...
15-Jul-2010
informa healthcare, 2010, Vol. 5, No. 7 , Pages 655-671, doi:10.1517/17460441.2010.493935 published on 15.07.2010
informa healthcare, online article

Importance of the field: Peptides are promising candidates as therapeutic agents due to their wide involvement in physiological processes. However, their often non-selective activity and their poor drug-like properties, mainly their inherent low stability to enzymatic degradation and poor oral bioavailability, limit their clinical potential. Somatostatin is a ...
06-Jul-2010
JBC, 2010, doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.126185, 28893-28901 published on 06.07.2010
JBC, online article
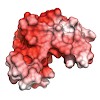
Sam68 (Src-associated during mitosis, 68 kDa) is a prototypical member of the STAR (signal transducer and activator of RNA) family of RNA-binding proteins. STAR proteins bind mRNA targets and modulate cellular processes such as cell cycle regulation and tissue development in response to extracellular signals. Sam68 has been shown to modulate alternative splicing ...
25-Jun-2010
The translational apparatus of the bacterial cell remains one of the principal targets of antibiotics for the clinical treatment of infection worldwide. Since the introduction of specific translation inhibitors into clinical practice in the late 1940s, intense efforts have been made to understand their precise mechanisms of action. Such research has often ...
28-May-2010
Nucleic Acids Research, 2010, doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq447, Vol. 38, No. 19 6707–6718 published on 28.05.2010
Nucleic Acids Research, online article
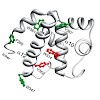
The plasmid pRN1 encodes for a multifunctional replication protein with primase, DNA polymerase and helicase activity. The minimal region required for primase activity encompasses amino-acid residues 40–370. While the N-terminal part of that minimal region (residues 47–247) folds into the prim/pol domain and bears the active site, the structure and function of ...
27-May-2010
Chemistry & Biology, 2010, 17 (DOI 10.1016/j.chembiol.2010.04.008), 504-14 published on 27.05.2010
Chemistry & Biology, online article
Accumulating evidence suggests that, during translation, nascent chains can form specific interactions with ribosomal exit tunnel to regulate translation and promote initial folding events. The clinically important macrolide antibiotics bind within the exit tunnel and inhibit translation by preventing progression of the nascent chain and inducing peptidyl-tRNA ...
21-May-2010
Diverse steps in gene expression are tightly coupled. Curiously, the La-motif-containing protein Sro9 has been shown to play a role in transcription and translation. Here, we show that Sro9 interacts with nuclear and cytoplasmic protein complexes involved in gene expression. In addition, Sro9 shuttles between nucleus and cytoplasm and is exported from the nucleus ...
19-May-2010

Ten years after the determination of the RNA polymerase II structure, the basic mechanism of mRNA synthesis during gene transcription is known. In the future, the initiation and regulation of transcription must be studied with a combination of structural biology, biochemistry, functional genomics, and computational methods. In this article, the efforts of our ...
14-May-2010
JACS, online article
Multiple N-methylation is a novel technology to improve bioavailability of peptides and increase receptor subtype selectivity. This technique has been applied here to the superpotent but nonselective cyclic peptide MT-II. A library of all possible 31 backbone N-methylated derivatives has been synthesized and tested for binding and activation at melanocortin ...
13-May-2010

A huge variety of proteins are able to form fibrillar structures, especially at high protein concentrations. Hence, it is surprising that spider silk proteins can be stored in a soluble form at high concentrations and transformed into extremely stable fibres on demand. Silk proteins are reminiscent of amphiphilic block copolymers containing stretches of ...
12-May-2010
JACS, 2010, DOI: 10.1021/ja1014508,, pp 7285–7287 published on 12.05.2010
JACS, online article

The measurement of 13C directed-detected paramagnetic relaxation enhancements (PREs) on spin-labeled proteins combines the efficacy of PREs for the detection of long-range distance information with the favorable sensitivity and resolution of 13C direct-detected experiments. The 13C PREs provide long-range distance restraints to map binding interfaces in proteins ...
01-May-2010
Cilengitide, a cyclic RGD pentapeptide, is currently in clinical phase III for treatment of glioblastomas and in phase II for several other tumors. This drug is the first anti-angiogenic small molecule targeting the integrins alphavbeta3, alphavbeta5 and alpha5beta1. It was developed by us in the early 90s by a novel procedure, the spatial screening. This ...
29-Apr-2010
RNA, 2010, doi:10.1261/rna.2009910, 1205-1216 published on 29.04.2010
RNA, online article

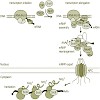
Small nuclear and small nucleolar RNAs (snRNAs and snoRNAs) are critical components of snRNPs and snoRNPs and play an essential role in the maturation of, respectively, mRNAs and rRNAs within the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. Complex and specific pathways exist for the assembly of snRNPs and snoRNPs, involving, for instance, nucleocytoplasmic transport of snRNAs ...
14-Apr-2010
Nucleic Acids Research, 2010, 5166-5176, doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq238 published on 14.04.2010
Nucleic Acids Research, online article

RNA exosomes are large multisubunit assemblies involved in controlled RNA processing. The archaeal exosome possesses a heterohexameric processing chamber with three RNase-PH-like active sites, capped by Rrp4- or Csl4-type subunits containing RNA-binding domains. RNA degradation by RNA exosomes has not been studied in a quantitative manner because of the complex ...
31-Mar-2010
Chemistry - A European Journal, online article
Local energetic effects of amino acid replacements are often considered to have only a moderate influence on the backbone conformation of proteins or peptides. As these effects are difficult to determine experimentally, no comparison has yet been performed. However, knowledge of the influence of side chain mutations is essential in protein homology modeling and ...
02-Mar-2010
Nucleic Acids Research, 2010, doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq135, 4040–4051 published on 02.03.2010
Nucleic Acids Research, online article
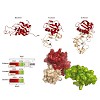
Spt5 is the only known RNA polymerase-associated factor that is conserved in all three domains of life. We have solved the structure of the Methanococcus jannaschii Spt4/5 complex by X-ray crystallography, and characterized its function and interaction with the archaeal RNAP in a wholly recombinant in vitro transcription system. Archaeal Spt4 and Spt5 form a ...
17-Feb-2010
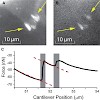
Spatial patterning of biochemical cues on the micro- and nanometer scale controls numerous cellular processes such as spreading, adhesion, migration, and proliferation. Using force microscopy we show that the lateral spacing of individual integrin receptor-ligand bonds determines the strength of cell adhesion. For spacings R90 nm, focal contact formation was ...
12-Feb-2010
Molecular Cell, online article
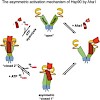
The chaperone Hsp90 is an ATP-dependent, dimeric molecular machine regulated by several cochaperones, including inhibitors and the unique ATPase activator Aha1. Here, we analyzed the mechanism of the Aha1-mediated acceleration of Hsp90 ATPase activity and identified the interaction surfaces of both proteins using multidimensional NMR techniques. For maximum ...
10-Feb-2010
Angewandte Chemie, online article
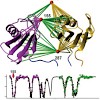
Puzzle-Arbeit: Eine effiziente, allgemein anwendbare Methode zur Bestimmung der Struktur von Proteinkomplexen und Mehrdomänenproteinen in Lösung mithilfe der NMR-Spektroskopie wird vorgestellt. Ausgehend von den bekannten hochaufgelösten Strukturen einzelner Domänen oder Untereinheiten wird die Domänenanordnung des Gesamtsystems aus NMR-Daten abgeleitet, die auch ...
α-Helical nascent polypeptide chains visualized within distinct regions of the ribosomal exit tunnel
07-Feb-2010
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, online article

As translation proceeds, the nascent polypeptide chain passes through a tunnel in the large ribosomal subunit. Although this ribosomal exit tunnel was once thought only to be a passive conduit for the growing nascent chain, accumulating evidence suggests that it may in fact play a more active role in regulating translation and initial protein folding events. Here ...
05-Feb-2010
Nucleic Acids Research, 2010, doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq038 published on 05.02.2010
Nucleic Acids Research, online article
Structural Maintenance of Chromosomes (SMC) proteins are vital for a wide range of processes including chromosome structure and dynamics, gene regulation and DNA repair. Eukaryotes have three SMC complexes, consisting of heterodimeric pairs of six different SMC proteins along with several specific regulatory subunits. In addition to their other functions, all ...
31-Jan-2010
Nucleic Acids Research, 2010, doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq029, published on 31.01.2010
Nucleic Acids Research, online article
Mediator is the central coactivor complex required for regulated transcription by RNA polymerase (Pol) II. Mediator consists of 25 subunits arranged in the head, middle, tail and kinase modules. Structural and functional studies of Mediator are limited by the availability of protocols for the prep- aration of recombinant modules. Here, we describe protocols for ...
29-Jan-2010
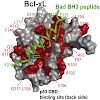
p53 can induce apoptosis through mitochondrial membrane permeabilization by interaction of its DNA binding region with the anti-apoptotic proteins BclxL and Bcl2. However, little is known about the action of p53 at the mitochondria in molecular detail. By using NMR spectroscopy and fluorescence polarization we characterized the binding of wildtype and mutant p53 ...
14-Jan-2010
Nature, online article
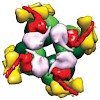
Form I Rubisco (ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase), a complex of eight large (RbcL) and eight small (RbcS) subunits, catalyses the fixation of atmospheric CO2 in photosynthesis. The limited catalytic efficiency of Rubisco has sparked extensive efforts to re-engineer the enzyme with the goal of enhancing agricultural productivity. To facilitate such ...
11-Dec-2009
Inhibitors targeting the integrin avb3 are promising new agents currently tested in clinical trials for supplemental therapy of glioblastoma multiforme (GBM). The aim of our study was to evaluate 18F-labeled glycosylated Arg-Gly-Asp peptide ([18F]Galacto-RGD) PET for noninvasive imaging of avb3 expression in patients with GBM, suggesting eligibility for this kind ...
13-Jul-2009
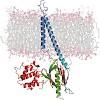
The formation of multicellular organisms requires concerted action by cells, which alter their adhesive and migratory behaviors. Cell adhesion and migration are tightly regulated by intra- and extracellular signals, which are conveyed through the cellular membrane by specialized receptors known as integrins. Integrins are the starting point of a variety of ...
12-May-2009
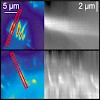
Focal adhesions are the anchoring points of cells to surfaces and are responsible for a large number of surface sensing processes. Nanopatterning studies have shown physiological changes in fibroblasts as a result of decreasing density of external binding ligands. The most striking of these changes is a decreased ability to form mature focal adhesions when ...