A Mass Spectrometry Platform for a Streamlined Investigation of Proteasome Integrity, Posttranslational Modifications, and Inhibitor Binding
19-Mar-2015
Chemistry & Biology, 2015, DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.chembiol.2015.01.004, Volume 22, Issue 3, p404–411, published on 19.03.2015
Chemistry & Biology, online article
Chemistry & Biology, online article
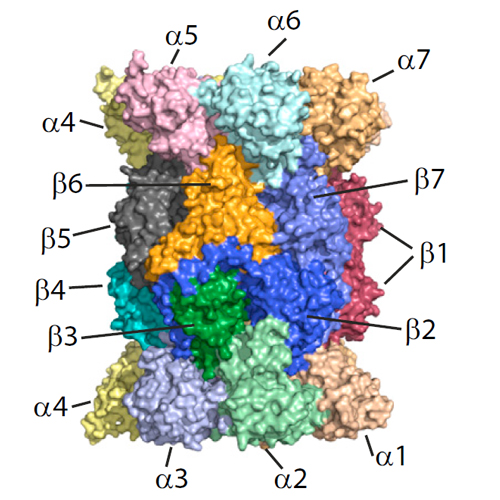
The proteasome is responsible for the majority of protein degradation within eukaryotic cells and proteasome inhibitors have gained blockbuster status as anticancer drugs. Here, we introduce an analytical platform comprising reverse phase chromatography, intact protein mass spectrometry, and customized data analysis that allows a streamlined investigation of proteasome integrity and posttranslational modifications. We report the complete mass spectrometric assignment of all subunits of the yeast core particle, as well as of the human constitutive 20S proteasome and the human immunoproteasome, including phosphorylated isoforms of α7. Importantly, we found several batches of commercially available immunoproteasome to also contain constitutive catalytic subunits. Moreover, we applied the method to study the binding mechanisms of proteasome inhibitors, both validating the approach and providing a direct readout of subunit preferences complementary to biochemical methods. Collectively, our platform facilitates an easy, reliable and comprehensive detection of different types of covalent modifications on multisubunit protein complexes with high accuracy.